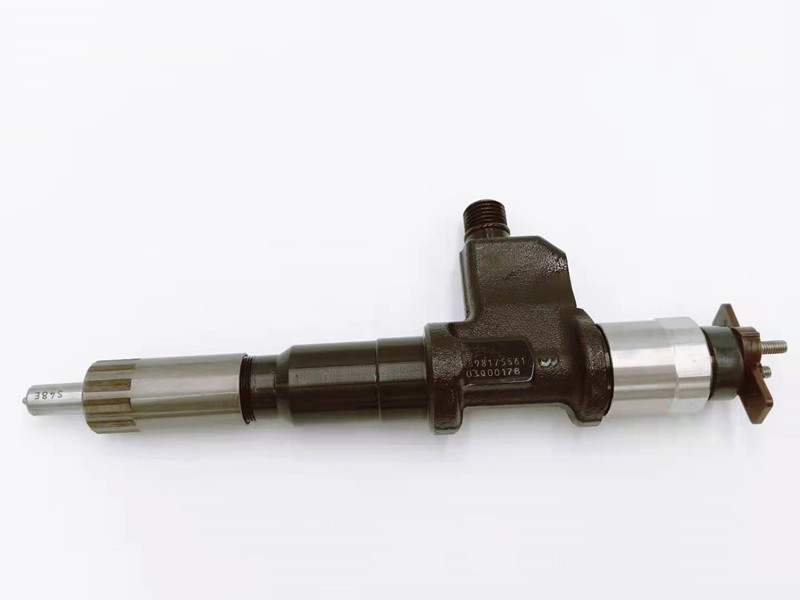
Diesel Injector Fuel Injector 095000-8981 Denso Injector for Isuzu
products detail



Used in Vehicles / Engines
| Product Code | 8981 |
| Engine Model | 4HK1-T |
| Application | Isuzu |
| MOQ | 6 pcs / Negotiated |
| Packaging | White Box Packaging or Customer's Requirement |
| Warranty | 6 months |
| Lead time | 7-15 working days after confirm order |
| Payment | T/T, PAYPAL, as your preference |
Mechanism of injector carbon deposit formation
1) From the perspective of diesel engine working process
Caprotti et al.!7 believed that after the needle valve of the direct injection diesel engine injector is closed, there is a small amount of diesel residue in the injection hole, and the cylinder expands to do work, resulting in an increase in the temperature in the cylinder, and the diesel diffuses to the outlet of the injection hole and the fuel injector. At the top, a liquid oil film is formed; the high temperature in the combustion chamber causes the fuel components to evaporate, and the fuel undergoes high-temperature cracking reactions to form viscous carbon deposits; the soot, high-boiling hydrocarbons and lubricating oil components generated during the combustion process are on the surface of the carbon deposits. Accumulation, the high diffusion rate of diesel oil, the soot environment in the combustion chamber and other factors ensure the speed of carbon deposit formation; the existence of soot makes the temperature of the top of the injector always high, effectively hindering the impact of liquid fuel on carbon deposits.
2) From the perspective of elemental analysis, Lepperhoff et al. found that the main components of carbon deposits were organic materials (carbon, hydrocarbons, oxygen and nitrogen) and a small amount of inorganic elements (sulfur, ), through elemental analysis of carbon deposits; wall and oil The contact medium of droplets is a necessary condition for the formation of carbon deposits. Most of the contact media are hydrocarbons with high boiling points. The formation process of carbon deposits can be divided into two processes: the induction period and the growth period, as shown in Figure 1. Among them: (1) During the induction period of carbon deposition, due to the low temperature of the wall surface, hydrocarbons with high boiling points are condensed to form a viscous film on the wall surface, and tiny particles are adsorbed due to the sticky paper effect; (2) During the growth period of carbon deposition, particles and other viscous substances are continuously adsorbed. The thickness of carbon deposition increases and the encouragement effect causes the surface temperature of carbon deposition to increase and the binding force to decrease, which limits the addition of more particles. At the same time, the flow fluctuation of gas causes The viscosity of the carbon deposit increases. Once the carbon deposit is attached to the wall, under the influence of long-term high temperature, chemical reactions such as decomposition, dehydration, and polymerization will occur, and the carbon deposit layer will be further compacted.



















